Model predictive control of thermally-activated building systems
master thesis, 2017
Optimizing HVAC (Heating, Ventilation & Air Conditioning) systems in buildings is a necessary step in reducing global energy consumption. Increasing HVAC efficiency through the use of modern insulation materials and implementation of advanced control algorithms are some of the ways through which such optimization can be achieved.
This thesis describes the principles of mathematical modelling of a house equipped with floor heating, electrical heating, and ceiling cooling, based on an analogy of thermodynamic processes with RC networks. The obtained mathematical model is used in the design of the model predictive controller that regulates house temperature by predicting future states of the model, while relying on current model states and the weather forecast. A comparison with conventional PI control shows improvements in terms of both energy consumption and achieved comfort.
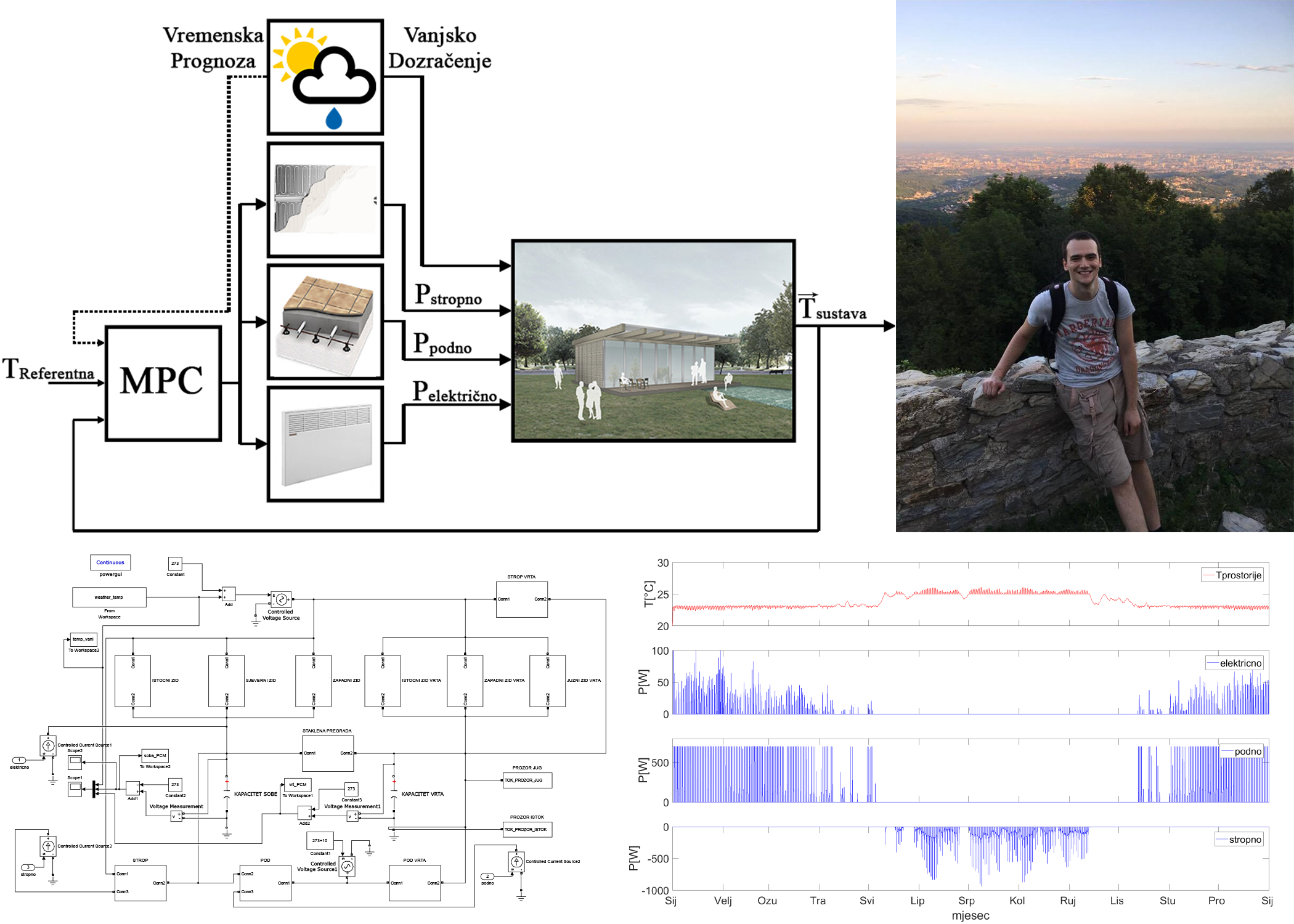
Keywords: floor heating; electrical heating; ceiling cooling; Simulink; RC-network; MPC



 Pristupačnost
Pristupačnost